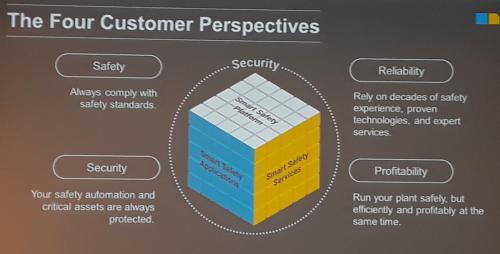
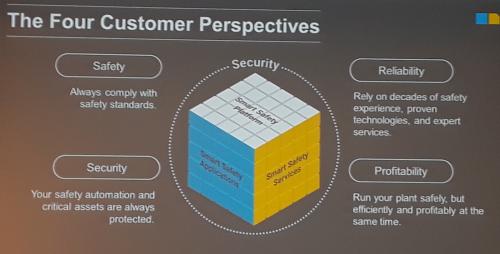
Manufacturing and process facilities are taking advantage of trends cybersecurity to make their applications more secure, with lower risk, greater profitability, and more flexibility. Highlights from 2019 ARC Forum media meetings reflect trends driving new product announcements.
Smarter safety with cybersecurity: Hima
Dr. Alexander Horch, vice president of R&D and product development for Hima, explained the importance of integrating scalable safety with cybersecurity with hardware and software, including firmware and communications. Such integration reduces complexity so operators can buy and use only what’s needed. This helps lower costs in one application with more than 60% savings in engineering and testing.
Such changes can be achieved while leaving cabling and input/output level unchanged, with less engineering. Stronger encryption of communications between controllers is under consideration as part of IEC 61784-3, edition 4, Horch said. Hima’s partnership with genua, (a cybersecurity firm purchased recently by the German treasury) is helping develop communications and kernels with less risk.
Intrinsic security: Bedrock Automation
Albert Rooyakkers, founder and CEO, Bedrock Automation, noted trends including the need for intrinsic security, legacy systems protection, easier communications, and better managed human access to controls.
Cybersecurity: Honeywell
Sam Wilson, global product marketing manager, Honeywell Industrial Cybersecurity, discussed big risks ranging from small, removable devices to industrial cybersecurity. Common and overlooked cyber threats and customer experiences are helping to shape Honeywell Process Solutions’ technological and software developments for industrial cybersecurity.

Wilson said USB devices can maliciously act like a keyboard, contain a mini-computer, and launch attacks. The dirty little secret is USB-type attacks go beyond malware and extends to devices. Attributes to have in cybersecurity implementations include:
- Inability to bypass safeguards
- Enterprise visibility and reporting so all instances can be seen globally
- Establish and follow good USB basic practices
- Enforce technical controls
- Monitor and manage network traffic (talking to other hosts)
- Regular and rapid anti-virus updates
- Patch and harden end nodes
- Consider restricting personal USB devices
- Deploy and test backup and recovery.
Using a Honeywell cybersecurity hardware and software technology, at a customer with 50 oil & gas locations, 44% detected and blocked at least one suspicious file; and 11% would not have been detected by traditional anti-virus software.
Mark T. Hoske is content manager, Control Engineering, CFE Media, mhoske@cfemedia.com.
KEYWORDS: Cybersecurity
ARC Forum 2019 included manufacturing and process trends.
Cybersecurity remains among the key trends impacting manufacturing.
More frequent updates can help lower risks.
CONSIDER THIS
Are you integrating new designs and technologies quickly enough to accelerate faster than your competitors?
See additional cybersecurity strategy stories including:
Cybersecurity certification may soon be required for manufacturers
Cybersecurity certification may soon be required for manufacturers
Strategic IT service company recognized by cybersecurity accreditation board
NeoSystems, a strategic IT service company, recognized with CMMC certification
Mitigating OT cybersecurity risks, enforcing best practices
Original content can be found at Control Engineering.
Do you have experience and expertise with the topics mentioned in this article? You should consider contributing content to our CFE Media editorial team and getting the recognition you and your company deserve. Click here to start this process.