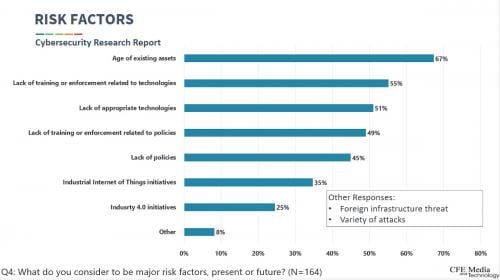
Those answering the 2020 Control Engineering cybersecurity research survey said, in a significant shift, the age of existing assets is the highest risk factor at 67%. In a similar 2016 cybersecurity survey, age of existing assets was 46% (third) in 2016. In 2016, the lack of appropriate technologies and lack of training or enforcement related to technologies were tied for first at 53%.
For the full report, click here to download.
With more remote operations related to the COVID-19 pandemic, and as manufacturing retools to lower human risk while ramping up again, cybersecurity remains a concern. Data was collected Feb. 7 through March 5.
Cybersecurity research: threats, vulnerabilities, training
Threat levels: Perceived cybersecurity threats within respondents’ organizations were 3% severe and 73% high or moderate. Perceived severity remains the same within margins of error for each study: 25% high, 48% moderate, 22% low, 3% severe.
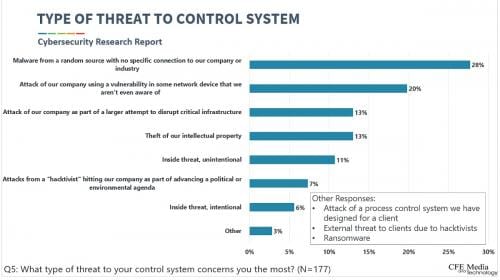
Most concerning threat: The most concerning threat to control systems is malware from a random source with no specific connection to our company or industry. The least concerning threat was an inside, intentional threat.
Greatest concern: Computer assets running commercial operating systems are the greatest concern regarding cybersecurity within the organization for 65% of respondents. The next greatest concerns were network devices and wireless communication devices.
Vulnerable components: Of the respondents, 39% said they are aware of zero malicious cyber incidents in the past 24 months while only 9% said they are aware of more than five malicious cyber incidents in the past 24 months.
Malicious incidents: The largest share of respondents, 40%, said cyber incidents they were aware of were accidental infections; while only 22% said were targeted in nature.
Accidental incidents: More than half of the respondents said they were allowed to report cyber-related incidents, and they did. Of the respondents, 20% said they were allowed and did not report the incident.
Incident response team: An operating operational incident response team was present in the organization for 50% of the respondents; however, about a third (34%) said their organization does not have such a response team.
Training: Training to identify things that may indicate a cyber incident or attack was received by 64% of respondents. Training regarding who to contact in the event of a cyber incident or attack was received by 50% of respondents and 49% said they receive training on identifying social engineering attacks. Training on any of these topics was not received by 14% of respondents.
Think again about opportunities for upgrades and to decrease risk with more remote workers and as more manufacturers and engineering-related businesses restart.
Mark T. Hoske is content manager, Control Engineering, CFE Media, [email protected].
RELATED ARTICLES
Engineering researchers form partnership focused on cybersecurity
https://www.industrialcybersecuritypulse.com/engineering-researchers-form-partnership-focused-on-cybersecurity/
Computer chip wins cybersecurity bounty
https://www.industrialcybersecuritypulse.com/computer-chip-wins-cybersecurity-bounty/
Researchers working on automating fleet of drones
https://www.industrialcybersecuritypulse.com/researchers-working-on-automating-fleet-of-drones/
Original content can be found at Control Engineering.
Do you have experience and expertise with the topics mentioned in this article? You should consider contributing content to our CFE Media editorial team and getting the recognition you and your company deserve. Click here to start this process.








