As the USA prepared for a holiday weekend ahead of the Fourth of July, the ransomware group REvil was leveraging a vulnerability in Kaseya software to attack managed service providers (MSPs) and their downstream customers. At least 1,500 companies appear to have been affected, even ones with no direct relationship to Kaseya.
At the time of writing, it appears a zero-day vulnerability was used to gain access to the Kaseya virtual system administrator (VSA) servers, before deploying ransomware on the endpoints managed by those VSA servers. This modus operandi vastly differs from previous ransomware campaigns, which have traditionally been human-operated, direct intrusions.
The analysis below offers Darktrace’s insights into the campaign by looking at a real-life example. It highlights how self-learning artificial intelligence (AI) detected the ransomware attack, and how Antigena protected customer data on the network from being encrypted.
Dissecting REvil ransomware from the network perspective
Antigena detected the first signs of ransomware on the network as soon as encryption had begun. The graphic below illustrates the start of the ransomware encryption over server message block (SMB) shares. When the graphic was taken, the attack was happening live and had never been seen before. As it was a novel threat, Darktrace stopped the network encryption without any static signatures or rules.
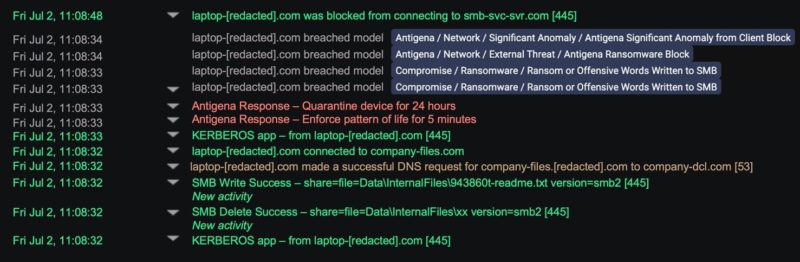
The ransomware began to take action at 11:08:32, shown by the “SMB Delete Success” from the infected laptop to an SMB server. While the laptop sometimes reads files on that SMB server, it never deletes these types of files on this particular file share, so Darktrace detected this activity as new and unusual.
Simultaneously, the infected laptop created the ransom note “943860t-readme.txt.” Again, the “SMB Write Success” to the SMB server was new activity – and crucially, Darktrace did not look for a static string or a known ransom note. Instead – by previously learning the “normal” behavior of every entity, peer group and the overall enterprise – it identified the activity was unusual and new for this organization and device.
By detecting and correlating these subtle anomalies, Darktrace identified this as the earliest stages of ransomware encryption on the network, and Antigena took immediate action.

Antigena took two precise steps:
- Enforce “pattern of life” for five minutes: This prevented the infected laptop from making any connections that were new or unusual. In this case, it prevented any further new SMB encryption activity.
- Quarantine device for 24 hours:Usually, Antigena would not take such drastic action, but it was clear this activity closely resembled ransomware behavior, so Antigena decided to quarantine the device on the network completely to prevent it from doing any further damage.
For several minutes, the infected laptop kept trying to connect to other internal devices via SMB to continue the encryption activity. It was blocked by Antigena at every stage, limiting the spread of the attack and mitigating any damage posed via the network encryption.

On a technical level, Antigena delivered the blocking mechanisms via integrations with native security controls such as existing firewalls, or by taking action itself to disrupt the connections.
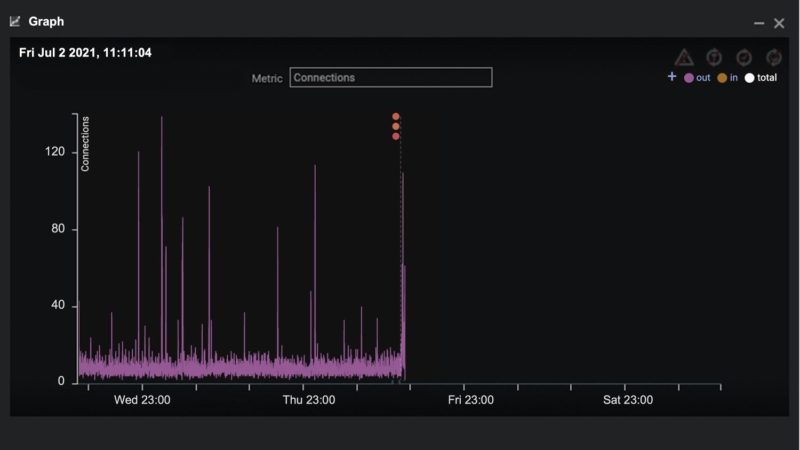
The below graphic shows the “pattern of life” for all network connections for the infected laptop. The three red dots represent Darktrace’s detections and pinpoint the exact moment in time when REvil ransomware was installed on the laptop. The graphic also shows an abrupt stop to all network communication as Antigena quarantined the device.
Attacks like REvil will always get in
During the incident, part of the encryption happened locally on the endpoint device, which Darktrace had no visibility over. Furthermore, the Internet-facing Kaseya VSA server that was initially compromised was not visible to Darktrace in this case.
Nevertheless, self-learning AI detected the infection as soon as it reached the network. This shows the importance of being able to defend against active ransomware within the enterprise. Organizations cannot rely solely on a single layer of defense to keep threats out. An attacker will always – eventually – breach your environment. Defense therefore needs to change its approach toward detecting and mitigating damage once an adversary is inside.
Many cyberattacks succeed in bypassing endpoint controls and begin to spread aggressively in corporate environments. Autonomous Response can provide resilience in such cases, even for novel campaigns and new strains of malware.
Thanks to self-learning AI, ransomware from the REvil attack could not perform any encryption over the network, and files available on that network were saved. This included the organization’s critical file servers, which did not have Kaseya installed and thus did not receive the initial payload via the malicious update directly. By interrupting the attack as it happened, thousands of files on network shares were protected from being encrypted.
Further observations
Data exfiltration
In contrast to other REvil intrusions Darktrace has caught in the past, no data exfiltration has been observed. This is interesting as it differs from the general trend this last year where cyber-criminal groups generally focus more on the exfiltration of data to hold their victims to ransom, in response to companies becoming better with backups.
Bitcoin
REvil has demanded a total payment of $70 million in Bitcoin. For a group that tries to maximize their profits, this seems odd for two reasons:
- How do they expect a single entity to collect $70 million from potentially thousands of affected organizations? They must be aware of the massive logistical challenges behind this, even if they do expect Kaseya to act as a focal point for collecting the money.
- Since DarkSide lost access to most of the Colonial Pipeline ransom, ransomware groups have shifted to demanding payments in Monero rather than Bitcoin. Monero appears to be more difficult to track for law enforcement agencies. The fact REvil are using Bitcoin, a more traceable cryptocurrency, appears counterproductive to their usual goal of maximizing profits.
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS)
Darktrace also noticed that other, more traditional “big-game hunting” REvil ransomware operations took place over the same weekend. This is not surprising as REvil is running a ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) model, so it is likely some affiliate groups continued their regular big-game hunting attacks while the Kaseya supply chain attack was underway.
Unpredictable is not undefendable
The weekend of the Fourth of July experienced major supply chain attacks against Kaseya and, separately, against California-based distributor Synnex. Threats are coming from every direction – leveraging zero-days, social engineering tactics and other advanced tools.
The attack happened in milliseconds, faster than any human cybersecurity team could react. The case study above demonstrates how self-learning technology detects such attacks and minimizes the damage. It functions as a crucial part of defense-in-depth when other layers – such as endpoint protection, threat intelligence or known signatures and rules – fail to detect unknown threats.
– This article originally appeared on Darktrace’s blog. Darktrace is a CFE Media content partner
Do you have experience and expertise with the topics mentioned in this article? You should consider contributing content to our CFE Media editorial team and getting the recognition you and your company deserve. Click here to start this process.








